
Understanding Compensatory Leave in Malaysia: A Guide for Employers and HR Teams
In today’s dynamic work environment, not all roles adhere to the traditional 9-to-5 schedule. Employees in sectors such as retail, logistics, healthcare, and IT support often find themselves working on weekends, public holidays, or outside standard office hours to meet urgent demands or maintain operations.
But what happens when employees are required to work beyond their regular schedule?
This is where compensatory leave—also known as time-off-in-lieu (TOIL)—comes into play. This article will explain what compensatory leave is, how it works in Malaysia, and how employers can manage it effectively.
What Is Compensatory Leave?
Compensatory leave refers to paid time off granted to employees who work outside their contracted hours, typically during rest days, weekends, or public holidays. Rather than being compensated through overtime pay, these employees are offered leave days that they can use at a later time.
It is a common practice in industries with irregular shifts or unpredictable workloads. While not mandated under Malaysian labour law, compensatory leave can be implemented as part of an internal HR policy or contractual agreement to ensure fairness and support employee wellbeing.
How Compensatory Leave Works
Compensatory leave is usually provided when an employee is instructed to work during:
-
Public holidays
-
Weekends or official rest days
-
After normal working hours due to urgent operational needs
For instance, if an employee supports a product launch on a Saturday or resolves an IT system issue outside regular hours, they may be granted a replacement leave day during the week. However, such arrangements must be planned, approved, and documented properly.
Each organisation should define:
-
Who is eligible for compensatory leave
-
How many leave hours or days can be granted
-
Timeframe within which the leave must be utilised (e.g. within the same month or quarter)
-
Approval process and documentation procedure
Having a clearly documented internal policy avoids misunderstandings, ensures fairness, and protects both employer and employee interests.
Common Scenarios Where Compensatory Leave Applies
To better understand its practical application, here are some typical scenarios where compensatory leave may be granted:
-
Urgent Work Outside Office Hours
Employees in IT or operations may be called in during off-hours to resolve technical issues. Instead of overtime pay, they receive a day off in return. -
Weekend or Holiday Events
Teams involved in marketing, project coordination, or business development may be required to attend events on weekends. A weekday off may be offered to compensate. -
Public Holiday Shifts
Customer service agents or warehouse staff working on public holidays may be granted time-off-in-lieu instead of public holiday pay. -
Additional Shifts in Essential Services
Sectors like healthcare and hospitality often involve rotating shifts. Compensatory leave offers a fair balance when extra shifts are unavoidable.
Is Compensatory Leave Required by Law in Malaysia?
Under the Employment Act 1955, Malaysian employers are not legally obligated to offer compensatory leave unless it is specified in the employment contract or company policy. The law only outlines mandatory overtime pay rates for work on public holidays and rest days.
However, offering compensatory leave is a best practice adopted by many modern organisations as a gesture of goodwill and recognition. It supports flexible working arrangements, particularly in industries where continuous operations are essential.
Benefits of Compensatory Leave for Employers and Employees
When implemented properly, compensatory leave can provide significant benefits:
-
Supports Work-Life Balance
Employees can recharge after working extra hours, reducing burnout and improving overall satisfaction. -
Acknowledges Extra Effort
Offering time-off-in-lieu demonstrates that the company values and appreciates employees’ contributions. -
Reduces Overtime Costs
It offers a cost-effective alternative to overtime pay while still compensating employees fairly. - Promotes Transparency and Fairness
A well-documented policy ensures consistent application across departments and prevents disputes.

Key Elements of a Compensatory Leave Policy
If your company chooses to offer compensatory leave, a clear and well-documented policy is essential. It should cover:
-
Eligibility Criteria
Clearly define which roles or types of employees (e.g. shift workers, non-exempt staff) are entitled to compensatory leave. -
Timeframe for Usage
Specify the period within which the earned leave must be taken (e.g. within 30 or 60 days) to avoid leave accumulation and planning issues. -
Leave Application & Approval Process
Outline how employees can request leave, who approves it, and how requests are tracked. A simple digital request form or self-service HR portal works well. -
Rules on Carry-Forward or Forfeiture
State whether unused compensatory leave can be carried forward or will be forfeited if not used within the defined period. -
Accurate Leave Tracking
Ensure proper documentation through an HR management system to record leave balances, dates earned, and leave taken.
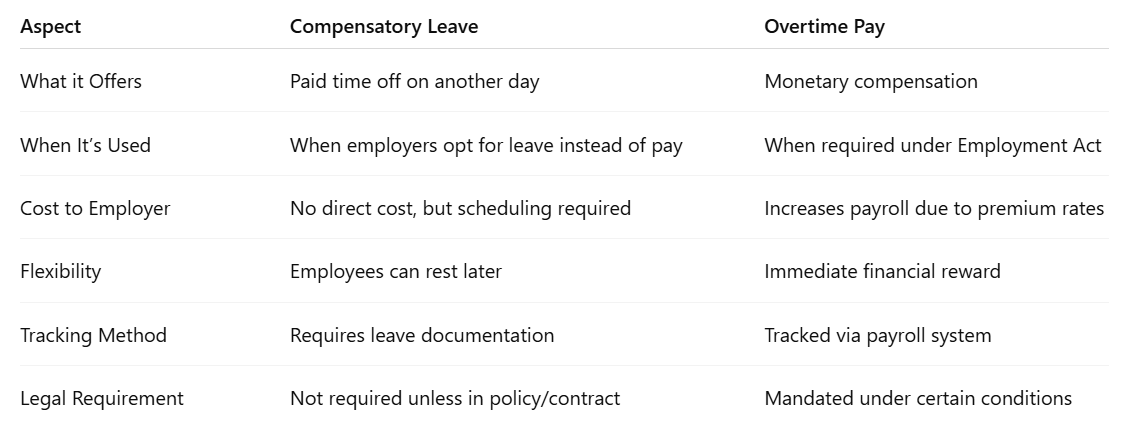
Compensatory Leave vs. Overtime Pay: Key Differences
Using HR Software to Simplify Compensatory Leave Management
Manual tracking of compensatory leave through spreadsheets or emails can lead to errors, delays, or disputes. By using an HR software solution like Pandahrms, HR teams can automate and streamline the entire process:
1. Automatic Tracking of Extra Hours
The system records when employees work beyond normal hours (e.g., weekends, public holidays), either through integrated attendance tracking or manual entries. It ensures accurate capture of eligible hours for compensatory leave.
2. Auto Calculation of Leave Entitlement
Based on company policies, the software can automatically convert extra working hours into compensatory leave credits — removing the need for manual calculations by HR.
3. Custom Policy Settings
HR can set up custom rules such as:
-
Which days qualify for compensatory leave
-
Expiry dates for unused leave
-
Approval workflows specific to compensatory leave
4. Employee Self-Service (ESS)
Employees can:
-
View their compensatory leave balance
-
Apply for time off directly in the system
-
Check approval status without chasing HR
5. Real-Time Manager Approvals
Supervisors get instant notifications and can approve or reject requests from anywhere — making the process faster and more transparent.
6. Accurate Leave Balances
The system updates leave balances in real-time after each approved request or new entitlement, helping avoid misuse or overuse.
7. Centralized Record Keeping & Audit Trail
All applications, approvals, and balances are stored in one place — making audits, compliance checks, or reviews much easier.
8. Reporting & Insights
Generate automated reports to analyze:
-
How many hours employees have worked extra
-
Compensatory leave usage trends
-
Department-level leave patterns
Tips for HR Teams
To ensure smooth implementation of compensatory leave, HR teams should:
-
Communicate the Policy Clearly
Include it in onboarding materials, employee handbooks, and internal portals. -
Maintain Consistency
Ensure that managers follow the same procedure across departments to avoid confusion or unequal treatment. -
Track and Audit Regularly
Use HR software or a leave log to monitor leave earned and taken. Regular reviews help maintain fairness and data accuracy. - Avoid Backlog
Encourage employees to take their leave within the stipulated period. Consider adding automatic alerts when leave is about to expire.




