As Malaysian workplaces evolve, maternity and paternity leave are no longer just compliance matters — they reflect how employers support working families, retain talent, and manage HR risk.
For HR teams and business owners, understanding the Employment Act 1955 (EA 1955) requirements is critical to avoid disputes, payroll errors, and legal exposure.
This guide provides a complete, up-to-date overview of maternity and paternity leave in Malaysia, including eligibility, duration, pay, employer obligations, and HR best practices — all explained clearly from an employer’s perspective.
Overview of Maternity and Paternity Leave in Malaysia
Under the Employment Act 1955, eligible employees in Malaysia are entitled to statutory parental leave benefits designed to protect family well-being while ensuring workplace fairness and continuity.
These provisions apply to:
-
Maternity leave for female employees
-
Paternity leave for married male employees (introduced via amendments)
Employers are legally required to comply with these provisions.
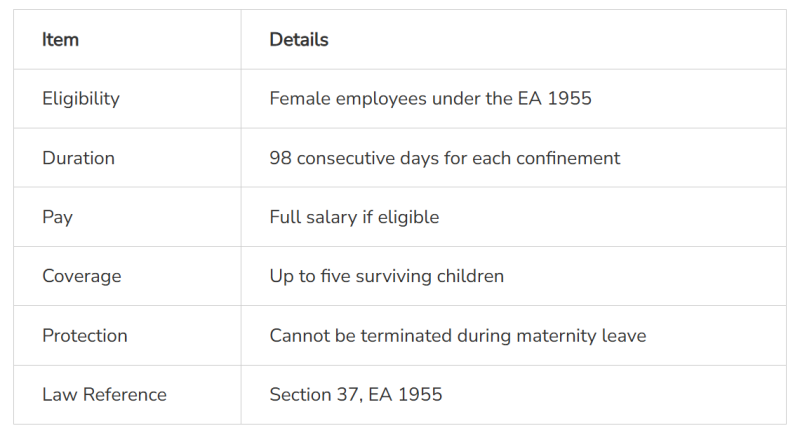
What Is Maternity Leave?
Maternity leave is a statutory entitlement that allows a female employee time off before and after childbirth to recover, care for her newborn, and return to work safely.
It is governed under Section 37 of the Employment Act 1955 and applies to eligible employees across most sectors.
Duration of Maternity Leave in Malaysia
As of current Malaysian law:
-
98 consecutive days of paid maternity leave
-
Leave may commence up to 30 days before the expected delivery date
-
The remaining days are taken after childbirth
-
Public holidays or rest days falling within this period are counted as part of the 98 days
Key Maternity Leave Facts (Malaysia)
What Is Maternity Allowance?
Maternity allowance ensures employees continue to receive income during maternity leave, preventing financial hardship during confinement and recovery.
Eligibility for Maternity Allowance
A female employee is eligible if she:
-
Has worked at least 90 days in the 9 months before confinement, or
-
Was employed at any time in the 4 months immediately before confinement
-
Has fewer than five surviving children
How Much Is Maternity Allowance?
-
Equivalent to the employee’s normal monthly salary
-
Includes basic salary and regular allowances
-
Paid throughout the entire 98-day maternity leave period
Can Employers Terminate a Pregnant Employee?
Under Malaysian labour law, employers are strictly prohibited from terminating an employee due to pregnancy.
Termination is only permitted in limited circumstances, such as:
-
Wilful misconduct
-
Breach of contract
-
Closure of business operations
Even then, employers must follow proper due process and documentation.
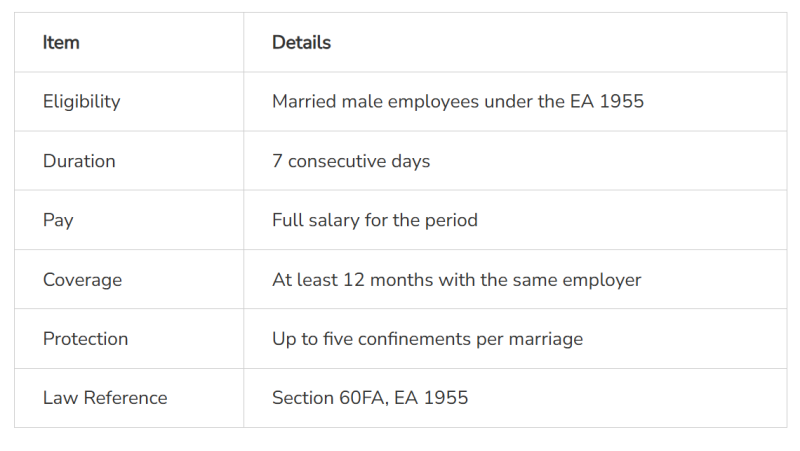
What Is Paternity Leave in Malaysia?
Paternity leave allows fathers to support their spouses and bond with their newborns during early parenthood.
Paternity leave was formally introduced under Section 60FA of the Employment Act 1955.
Duration of Paternity Leave in Malaysia
Eligible male employees are entitled to:
-
7 consecutive days of paid paternity leave
-
Must be legally married to the child’s mother
-
Must have served the same employer for at least 12 months
-
Leave must be taken within 60 days of childbirth
-
Applicable for up to five confinements per marriage
Key Paternity Leave Facts
Can Employers Refuse Maternity or Paternity Leave?
❌ No, if the employee meets statutory eligibility.
-
Employers cannot refuse maternity leave
-
Employers should not deny paternity leave without valid justification
-
Refusal may expose the company to complaints, penalties, or legal action
Why Maternity and Paternity Leave Matter for Employers
Parental leave is more than a legal obligation — it directly impacts:
-
Employee retention
-
Workplace morale
-
Employer branding
-
Long-term productivity
Modern employers in Malaysia increasingly:
-
Extend maternity benefits beyond statutory minimums
-
Offer additional paternity or parental leave
-
Introduce flexible return-to-work arrangements
These initiatives support shared caregiving responsibilities and position the company as a family-friendly employer.
HR Best Practices for Managing Maternity & Paternity Leave
To ensure compliance and smooth operations, employers should:
1. Establish Clear Leave Policies
Document maternity and paternity leave policies clearly in employee handbooks.
2. Communicate Early and Transparently
Encourage employees to notify HR early to allow for manpower planning.
3. Maintain Accurate Records
Proper documentation protects employers during audits and disputes.
4. Plan Workforce Coverage
Arrange temporary coverage to ensure business continuity.
5. Support Employees During Leave
Maintain professional communication and prepare structured return-to-work plans.
Common HR Questions (FAQ)
1. Can maternity leave start before childbirth?
Yes. Maternity leave may begin up to 30 days before the expected delivery date, subject to agreement.
2. Can paternity leave be taken before birth?
No. Paternity leave can only be taken after childbirth, within 60 days.
3. Are public holidays added on top of maternity leave?
No. Public holidays and rest days are included within the 98-day period.
4. What happens if an employee resigns during maternity leave?
They may lose maternity allowance entitlement, but notice period obligations still apply.
Simplify Maternity & Paternity Leave Management with Pandahrms
Managing parental leave manually increases the risk of:
-
Payroll miscalculations
-
Incomplete records
-
Compliance gaps
With Pandahrms, HR teams can:
-
Automate maternity and paternity leave applications
-
Ensure accurate payroll calculations
-
Maintain compliant leave records
-
Generate reports instantly for audits and reviews
A structured HR system allows employers to stay compliant while supporting employees professionally.
Conclusion
Maternity and paternity leave in Malaysia are not optional benefits — they are legal rights and HR responsibilities.
Employers who manage parental leave correctly:
-
Reduce legal risk
-
Build employee trust
-
Strengthen workplace culture
By understanding the Employment Act requirements and using an integrated HR system like Pandahrms, companies can manage parental leave confidently — with clarity, compliance, and care.




