The EA Form appears every year in HR updates, payroll reminders, and tax season checklists — but many employers and employees still misunderstand its purpose. Whether you’re issuing the form or using it to file income tax, getting the EA Form right is critical for compliance with LHDN (Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri Malaysia).
This guide breaks down what the EA Form is, why employers must issue it, key deadlines, common mistakes that trigger audits, and how HR teams can simplify the entire process using Pandahrms automated payroll features.
What Is the EA Form in Malaysia?
The EA Form — also known as Borang EA or C.P.8A — is an annual statement of remuneration that employers must issue to all employees.
It summarises:
-
Basic salary
-
Allowances & perquisites
-
Bonuses & commissions
-
Overtime payments
-
Benefits-in-kind (BIK)
-
Employer & employee statutory deductions (EPF, SOCSO, EIS, PCB/MTD)


Employees use the EA Form to complete their personal income tax filing (Form BE), while employers must issue it by 28 February each year.
Failing to issue the EA Form on time can lead to penalties under Section 83(1A) of the Income Tax Act 1967.
Why the EA Form Matters for Employers & Employees
The EA Form is a core compliance document.
For Employers
-
Confirms payroll accuracy
-
Ensures figures match CP39, CP8D and Form E
-
Reduces risk of LHDN audits
-
Protects the company from penalties
For Employees
-
Acts as proof of annual earnings
-
Ensures accurate income declaration
-
Helps verify PCB deductions
-
Required for Form BE submission
A properly prepared EA Form reflects strong HR governance and builds employee trust.
EA Form Deadlines & Related LHDN Forms
Employers must comply with strict statutory dates:
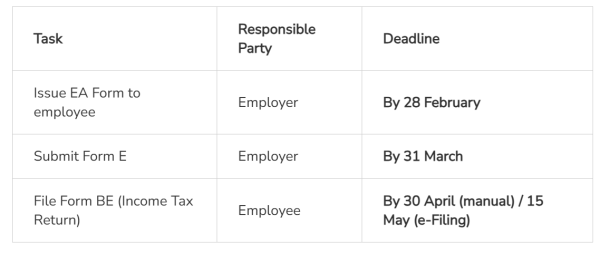
Missing these deadlines risks late submission penalties, especially for Form E.
Other Important Forms
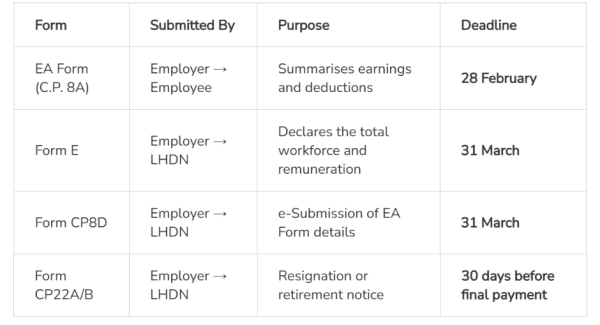
For HR teams, consolidating these forms early avoids the usual March–April rush.
How to Ensure Accuracy When Preparing the EA Form
Accuracy is the most important part of EA Form preparation.
HR should review:
-
Total annual salary
-
Allowances & perquisites (correct categories)
-
Overtime, commission, bonus
-
BIK & value of company-provided assets
-
PCB deducted each month
-
Employer contributions (EPF, SOCSO, EIS)
-
Employee status changes (resignations, transfers, unpaid leave)
Consistent payroll records throughout the year make the EA Form much easier to prepare — and significantly reduce compliance risks.
This is why many Malaysian SMEs rely on Pandahrms, where payroll, statutory contributions, EA, CP8D and Form E data are pulled directly from the system, reducing manual work and calculation errors.
Common EA Form Mistakes That HR Should Avoid
Even experienced payroll teams can make errors. The most common include:
1. Missing the 28 February Deadline
A statutory non-negotiable requirement.
2. Forgetting Resigned or Terminated Employees
EA Forms must still be issued for any employee who worked any period in the year.
3. Using Outdated EA Templates
Old templates = wrong fields, outdated tax categories, incorrect sequencing.
4. Incorrect Figures & Misclassified Allowances
Wrong categorisation often leads to:
-
Allowances placed under reimbursements
-
BIK missing
-
PCB not tallied with payroll
5. Mismatch Between EA, CP8D & Form E
LHDN checks all three. Inconsistencies trigger review or audit.
Using a centralised payroll system like Pandahrms helps ensure data alignment across EA, CP8D and Form E instantly.
What’s New for EA Form 2025/2026 Submissions?
As companies prepare EA Forms for income earned in 2025, here’s what HR should note:
-
EA Forms for 2025 earnings must be issued by 28 February 2026
-
Form E submission remains 31 March 2026
-
e-Data Praisi continues as LHDN’s preferred online submission method
-
Digital HR systems are now highly recommended due to audit trail requirements
HR teams should begin reviewing payroll records before year-end, not in February, to avoid bottlenecks.
How Pandahrms Simplifies EA Form Preparation
With Pandahrms:
-
EA Forms are auto-generated from payroll data
-
No manual templates, no formulas, no version errors
-
CP8D & Form E data are consolidated automatically
-
Employees can download EA Forms directly from the portal/mobile app
-
All payroll, PCB and statutory records remain synced and audit-ready
This reduces human error and frees HR to focus on planning — not paperwork.
Conclusion
The EA Form is more than a yearly tax document — it reflects the company’s payroll accuracy, compliance standards, and HR professionalism. Timely, accurate EA preparation prevents penalties, ensures transparent reporting, and helps both HR and employees manage tax season with confidence.
With Pandahrms, employers eliminate manual errors and streamline EA Form, CP8D and statutory compliance with a complete, audit-ready payroll solution.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Do employees submit the EA Form to LHDN?
No. Employers submit the payroll data through Form E/CP8D. Employees only use the EA Form when filing Form BE.
2. What if an employee works for two companies in the same year?
They will receive two EA Forms, one from each employer, covering their employment periods.
3. How can employers simplify EA Form preparation?
Use a digital HR system like Pandahrms.
EA, CP8D, PCB, allowances, deductions and statutory details are generated automatically and always aligned with LHDN requirements.
4. Do employers need to issue EA Forms for part-time, contract or resigned employees?
Yes — as long as the employee received remuneration during the year.
5. Is EA Form required for foreign workers?
Yes, if PCB is deducted or if they fall under taxable employment categories.




