(2026 Update) EA Form Malaysia: Complete Employer & Employee Guide to Tax Compliance
Navigating payroll and income tax compliance in Malaysia can be complex—especially when it comes to the EA Form (Borang EA / C.P.8A). Each year, this single document forms the foundation of employees’ personal income tax filings and represents a key statutory obligation for employers.
For the 2026 tax season (Year of Assessment 2025), accuracy, timely issuance, and regulatory compliance are more critical than ever. Errors, delays, or omissions may expose employers to enforcement action under the Income Tax Act 1967.
This comprehensive guide explains what the EA Form is, who must issue and receive it, key deadlines, penalties, and HR best practices—providing employers with a clear, practical reference to stay compliant and prepared.
What Is EA Form (C.P. 8A)?
The EA Form, officially known as Borang EA (C.P. 8A), is an Annual Remuneration Statement issued by employers to employees in Malaysia.
It summarises an employee’s total earnings and statutory deductions for a specific Year of Assessment (YA) and is required for individual income tax filing with LHDN.
Information Included in the EA Form
The EA Form consolidates a full year of payroll data, including:
-
Gross salary & wages (basic pay, overtime)
-
Bonuses & commissions
-
Allowances (taxable and tax-exempt)
-
Benefits-in-Kind (BIK) (company car, fuel, accommodation)
-
EPF (KWSP), SOCSO (PERKESO) & EIS – employee portion only
-
Monthly Tax Deduction (PCB / MTD) paid to LHDN
Why it matters:
Employees do not need to calculate income manually using 12 payslips—the EA Form is the official reference used for Borang BE e-Filing.
EA Form vs Form E vs CP8D (Common Payroll Confusion)
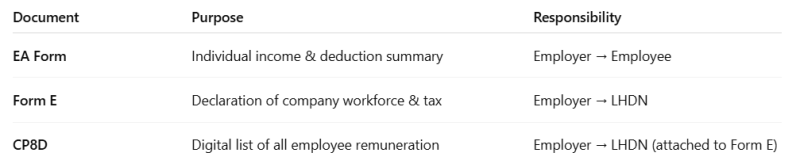
Key reminder: EA Form is not submitted to LHDN—but inaccuracies may still trigger audits if it doesn’t match CP8D data.
Who Needs to Receive the EA Form?
Employers are legally required to prepare and issue the EA Form (C.P.8A) to all employees who were employed during the Year of Assessment 2025, regardless of employment status or length of service.
This obligation applies to:
-
Current employees
-
Former employees who worked for the company at any time during 1 January 2025 to 31 December 2025
The EA Form must be issued to:
-
Full-time employees
-
Part-time employees
-
Contract employees under a contract of service
Even if an employee worked for only a short period during the year, the EA Form is still required as long as taxable employment income was paid.
Foreign Employees
Employers must also issue the EA Form to foreign workers who are employed under a contract of service, as they are treated as employees for tax reporting purposes.
However, if the individual is engaged as an independent contractor (not under a contract of service), the employer is generally required to issue Form CP58 instead of the EA Form.
Company Directors
Company directors are regarded as employees for tax purposes. Employers must therefore issue an EA Form to directors who received remuneration during the Year of Assessment.
EA Form Deadlines for 2026 (YA 2025)
Mark these critical tax dates to avoid penalties:
-
28 February 2026 – Deadline to issue EA Forms to employees
-
31 March 2026 – Deadline to submit Form E & CP8D
-
30 April 2026 – Form BE manual submission deadline
-
15 May 2026 – Form BE e-Filing deadline (with grace period)
Late issuance disrupts employees’ tax filing and exposes employers to legal action.
How Employees Use EA Form for Tax Filing
Employees use the EA Form when completing Borang BE via MyTax, including:
-
Total employment income (EA Form Section B)
-
Tax reliefs (EPF, SOCSO deductions)
-
PCB paid (to avoid double taxation)
Any mismatch between EA Form and MyTax records can trigger LHDN queries.
What Are the Penalties for Late Submission or Non-Compliance?
Failure to issue the EA Form is a serious offence under Section 120 of the Income Tax Act 1967.
- Fines: Between RM200 and RM20,000.
- Imprisonment: Up to 6 months
- Both: In severe cases, employers may face both financial penalties and jail time.
In addition, inconsistencies between an employee’s EA Form and the employer’s CP8D submission may raise red flags with LHDN and potentially trigger a tax audit.
Download Your Free EA Form Templates (2025)

Step-by-Step Guide on Submitting and Printing EA Form for Employers (YA 2025)
Employers may generate the EA Form 2025 (C.P.8A) using a payroll system or manual templates. Regardless of the method used, accuracy and timely submission are critical to meet statutory requirements under the Income Tax Act 1967.
Below is a practical step-by-step guide to help employers submit and distribute EA Forms correctly for the 2026 tax filing season (Year of Assessment 2025).
Step 1: Gather Employee Income Records
Before issuing EA Forms, employers must compile complete payroll records for each employee covering the period from 1 January 2025 to 31 December 2025.
This includes:
-
Basic salary and wages
-
Bonuses and incentives
-
Allowances and benefits-in-kind
-
Statutory deductions such as PCB, EPF, SOCSO, EIS, and Zakat (if applicable)
Ensuring accurate payroll data at this stage reduces errors and reconciliation issues later.
Step 2: Generate or Download EA Form Template
Most employers rely on payroll software to automatically generate EA Forms based on yearly payroll data.
Alternatively, employers may:
-
Download LHDN’s official EA Form (C.P.8A) template
-
Manually complete employee and income details
Regardless of the method, employers remain fully responsible for the accuracy of the information provided.
Step 3: Log in to the MyTax Portal
Once the EA Forms are prepared, employers must log in to the MyTax portal to submit the required employer filings.
Access the MyTax portal and:
-
Click Login
-
Enter your registered username and password
-
Use the “Forgot Password” function if access credentials need to be reset
Step 4: Access the e-Filing Section
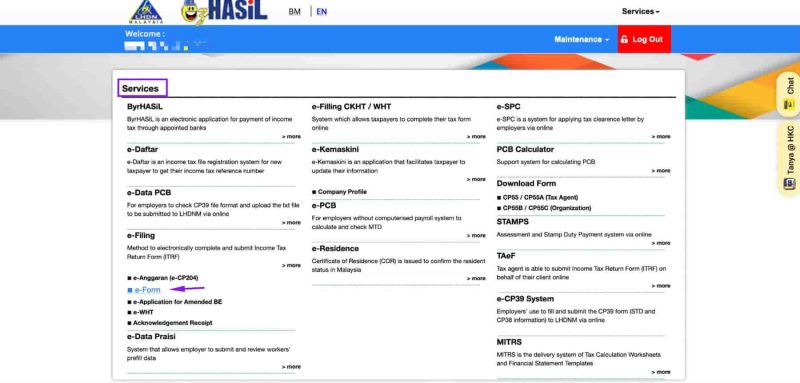
After logging in:
-
Click on “Services”
-
Select “e-Filing” from the menu.
-
Click on “e-Form” to proceed
This section is used for employer-related tax filings, including Form E submission.
Step 5: Select the Correct e-Form and Year of Assessment

Under the e-Form tab:
-
Select Non-Individual
-
Click on e-E Section (this is the section for Form E submission)
-
Choose the correct Year of Assessment: 2025
Selecting the correct YA is essential to avoid filing errors or rejection by LHDN.
Step 6: Complete Employer and Payroll Details
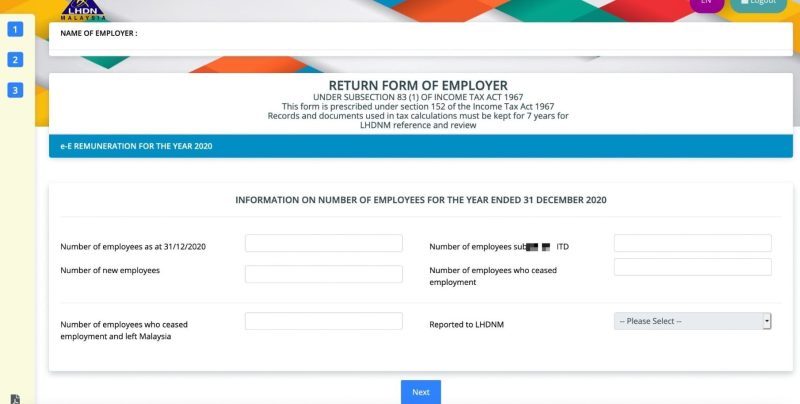
Within the e-Form E section, employers must provide the following information:
Company/Employer Information
-
Company name, registration number, and income tax reference number
-
Nature of business and industry
-
Employer contact details (address, phone, email, etc.)
Employee Details
-
Total number of employees for the year
-
Number of employees who received remuneration
-
Number of new hires and resignations during 2025
Salary and Tax Deduction Information
-
Total salary/wages paid to employees
-
Tax deductions (PCB, EPF, SOCSO, EIS, Zakat, etc.)
-
Statutory contributions (EPF, SOCSO, EIS)
-
Bonuses, allowances, and other taxable benefits
Ensure all figures align with payroll records and EA Forms issued to employees.
Step 7: Review and Sign the Declaration Form

Before submission:
-
Carefully review all entered information
-
Confirm accuracy and completeness
Click “Sign & Send” to declare that the information provided is true and correct.
This declaration is legally binding and should only be completed by authorised personnel.
Step 8: Submit, Print, and Distribute EA Forms
After submission:
-
A confirmation message will appear
-
Save or print the submission receipt for record-keeping
Once verified, employers should:
-
Print physical copies of EA Forms or
-
Distribute soft copies securely via email to employees
Employers are required to retain EA Forms and supporting records for at least seven (7) years for audit and compliance purposes.
Step 9: Check Submission Status
To confirm successful submission:
-
Go to MyTax Dashboard
-
Click on “e-Filing History”
-
Check the Form E submission status
This ensures the filing has been properly received and recorded by LHDN.
Handling Special Cases in EA Form Reporting
Even with payroll software, some cases need extra attention:
-
Mid-year joiners: Report income and deductions only for the period employed; prorated automatically by payroll systems.
-
Resigned employees: Include salary, final bonuses, and deductions up to the last working day.
-
Overseas or expatriates: Apply Malaysian tax rules for income, allowances, and tax-exempt items.
-
Multiple income sources: Consolidate all salaries, allowances, and benefits-in-kind into one accurate EA Form.
Tip: Always review special cases to prevent discrepancies and ensure compliance with LHDN.
Best Practices for EA Form Compliance in 2026
-
Automate payroll & EA Form generation
-
Reconcile PCB totals early (January check)
-
Validate BIK values carefully
-
Issue EA Forms digitally to reduce errors
-
Keep audit-ready payroll records
Why Payroll Software Matters for EA Forms
Manual EA Form preparation is time-consuming and error-prone.
Using an integrated HR & payroll system like Pandahrms helps employers:
-
Generate EA Forms automatically
-
Eliminate manual calculation errors
-
Stay compliant with LHDN updates
-
Store historical records securely
-
Prepare CP8D & Form E seamlessly
For HR teams, this means less compliance stress, fewer employee disputes, and audit-ready reporting.
Conclusion: EA Form Is Not Optional—It’s Critical
The EA Form is the foundation of Malaysia’s annual tax process. Employers who understand the 2026 requirements, meet deadlines, and ensure payroll accuracy protect their business while supporting employees’ tax compliance.
Early preparation isn’t just best practice—it’s risk management.
Need to simplify EA Form preparation for 2026?
Pandahrms helps employers generate compliant EA Forms effortlessly—accurate, automated, and audit-ready.




