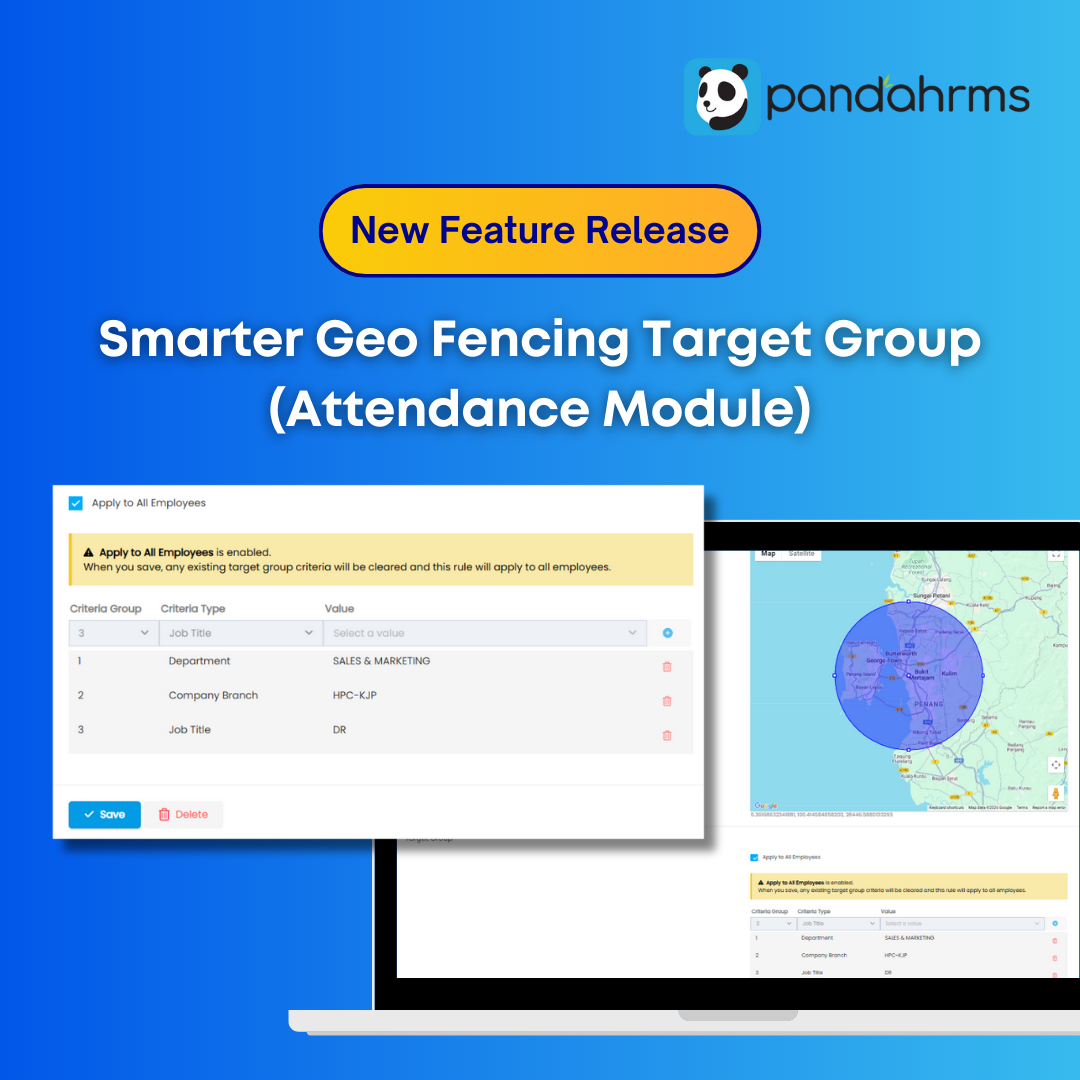
Malaysia has officially gazetted the Minimum Wages Order 2024, introducing a revised nationwide minimum wage framework that employers must comply with in 2025.
Effective in stages from 1 February 2025, this update applies to all states in Malaysia and affects most private sector employers, including those with foreign employees.
For HR leaders and business owners, understanding the new rates, timelines, and compliance obligations is critical to avoid penalties and payroll disputes.
New Minimum Wage Rate in Malaysia (2025)
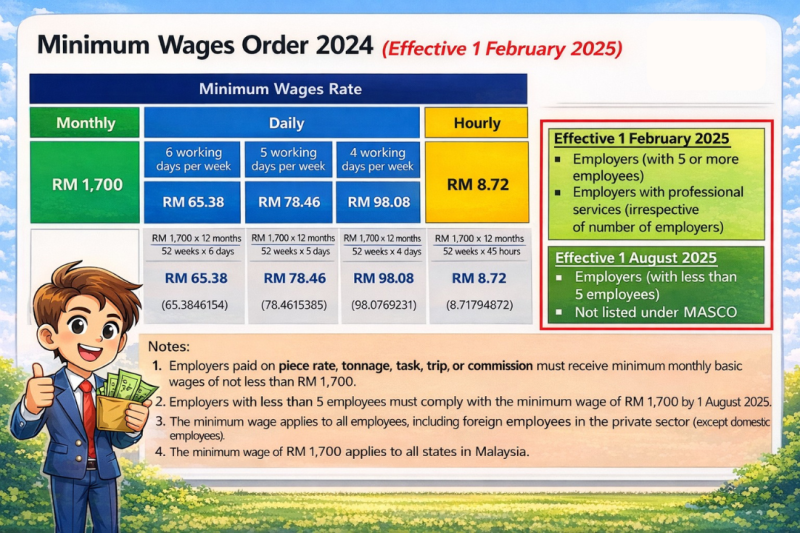
Under the Minimum Wages Order 2024, the minimum monthly wage is set at:
💰 RM 1,700 per month
This rate applies uniformly across all states in Malaysia, replacing previous regional wage structures.
Daily & Hourly Minimum Wage Rates
Based on the RM 1,700 monthly minimum wage, the equivalent daily and hourly rates are as follows:
Daily Minimum Wage
-
6 working days per week: RM 65.38
-
5 working days per week: RM 78.46
-
4 working days per week: RM 98.08
Hourly Minimum Wage
-
RM 8.72 per hour
These calculations are derived from the statutory formula using annual working days and hours.
Implementation Timeline: Who Must Comply and When?
✅ Effective 1 February 2025
The RM 1,700 minimum wage applies to:
-
Employers with 5 or more employees
-
Employers providing professional services, regardless of company size
✅ Effective 1 August 2025
The RM 1,700 minimum wage applies to:
-
Employers with fewer than 5 employees
-
Employers not listed under MASCO
This phased approach provides smaller businesses with a transition period to adjust payroll structures.
Who Is Covered Under the Minimum Wages Order 2024?
The minimum wage applies to:
-
All employees in the private sector
-
Foreign employees working in Malaysia
❌ Excluded:
-
Domestic employees (e.g. domestic helpers)
Important Compliance Notes for Employers
HR teams and employers should take note of the following key requirements:
-
Employees paid by piece rate, tonnage, task, trip, or commission must still receive a minimum basic monthly wage of RM 1,700
-
Payment structures must ensure total basic wages do not fall below the statutory minimum
-
Employers with fewer than 5 employees must comply by 1 August 2025
-
The minimum wage applies nationwide, with no state-based variations
Failure to meet these requirements may expose employers to enforcement action under Malaysian labour laws.
Why Minimum Wage Compliance Matters
Non-compliance with the Minimum Wages Order is an offence and may result in:
-
Fines
-
Backdated wage payments
-
Legal action and reputational risk
From an HR governance perspective, minimum wage compliance is not optional — it is a core employer obligation.
HR Best Practices: Preparing for Minimum Wage 2025
To ensure smooth compliance, employers should:
-
Review salary structures and employment contracts early
-
Recalculate daily and hourly rates for shift-based or part-time staff
-
Ensure payroll systems reflect the new statutory rates
-
Communicate wage adjustments clearly to employees
Using a centralised HR and payroll system helps reduce manual errors and ensures statutory compliance across the organisation.
Simplify Payroll Compliance with Pandahrms
Managing wage adjustments, payroll calculations, and compliance tracking can be complex — especially during regulatory changes.
Pandahrms helps employers:
-
Automate payroll calculations based on statutory minimum wages
-
Maintain accurate employee wage records
-
Reduce compliance risks through structured HR processes
-
Ensure timely and transparent salary payments
With the Minimum Wages Order 2024 coming into effect, having a reliable HR system is more important than ever.
Final Thoughts: Staying Compliant with Malaysia’s Minimum Wage
The Minimum Wages Order 2024 is now fully in force, and compliance is no longer optional. Employers must ensure that payroll structures, wage calculations, and payment practices meet the current minimum wage requirements across all states in Malaysia.
Regular payroll reviews are essential—not only to avoid penalties and enforcement action, but also to maintain employee trust and operational stability. This is especially important for employers managing different work schedules, wage types, or foreign employees.
By putting the right systems and controls in place, employers can stay compliant, reduce administrative risk, and focus on growing their business with confidence. A structured HR and payroll process is key to ensuring accuracy, transparency, and long-term compliance under Malaysia’s evolving labour regulations.