The Employment Insurance System (EIS) is not just another statutory deduction on the payslip. For Malaysian employers, it is a mandatory payroll compliance item that directly affects employee protection, termination processes, and post-employment support.
Managed by PERKESO, EIS provides short-term financial assistance and re-employment support to eligible private-sector employees who lose their jobs involuntarily. For HR and payroll teams, understanding how EIS works — and managing it correctly — is essential to avoid disputes, penalties, and employee dissatisfaction.
This guide explains what EIS is, who must contribute, how payroll calculations work, when employees can claim, and what HR should prepare, especially during terminations and retrenchments.
What Is EIS in Malaysia?
The Employment Insurance System (EIS) is Malaysia’s national employment insurance scheme introduced to support employees who lose their jobs through no serious fault of their own.
EIS provides:
-
Temporary income replacement
-
Job search and re-employment assistance
-
Training and upskilling support
EIS contributions are collected monthly through payroll and administered by PERKESO, alongside SOCSO.
From an employer’s perspective, EIS:
-
Is mandatory for eligible employees
-
Must be accurately calculated and paid on time
-
Forms part of the employee’s statutory protection after termination
Why Is There an EIS Contribution in Payroll?
EIS exists to ensure that employees who are retrenched, made redundant, or affected by business closure are not left without income or support while seeking new employment.
Who Must Contribute?
Most private-sector employees in Malaysia:
-
Aged 18 to 60
-
Employed under a contract of service
Key Employer Responsibilities
-
Deduct the employee portion via payroll
-
Contribute the employer portion
-
Display EIS clearly on the payslip
-
Remit contributions to PERKESO on time
This transparency protects both the employer and employee if a claim is required later.
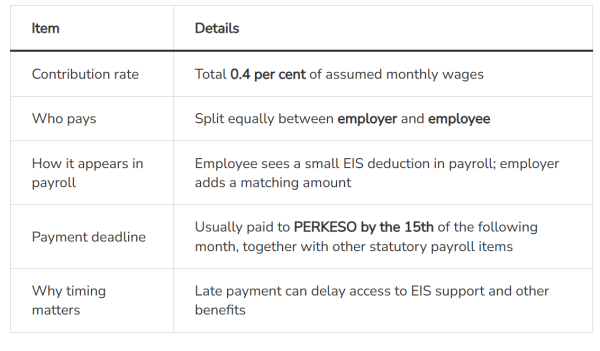
How Much Is the EIS Contribution?
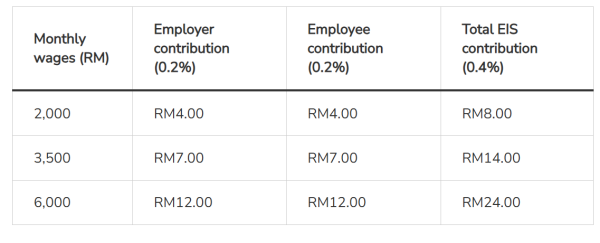
EIS contributions are 0.4% of assumed monthly wages, split equally.
EIS Contribution Summary
Example Calculation:
Why accuracy matters:
Late or incorrect EIS payments can delay employee claims, create disputes during termination, and expose employers to compliance issues.
When Can an Employee Claim EIS?
EIS is designed for involuntary loss of employment.
Common Eligible Situations
-
Retrenchment
-
Redundancy
-
Business closure
-
Constructive termination (subject to verification)
Situations Not Covered
-
Voluntary resignation
-
Dismissal due to serious misconduct
This distinction is important. Employers must ensure that termination letters clearly state the correct reason, as this directly affects claim eligibility.
What Benefits Do Employees Receive Under EIS?
EIS provides both financial support and re-employment assistance, not just cash payouts.
Key EIS Benefits
Job Search Allowance (JSA)
Temporary income support while actively seeking employment.
Reduced Income Allowance (RIA)
Partial income support for employees who lose one job but still have another, subject to contribution history.
Early Re-Employment Allowance (ERA)
Additional incentive for employees who secure new employment before the JSA period ends.
Training Fee (TF) & Training Allowance (TA)
Funding and allowance for approved training programmes to improve employability.
Job Matching & Career Services
Support through PERKESO’s employment services, referrals, and guidance.
HR Checklist: When an Employee Loses Their Job
Before the Last Working Day
-
Verify EIS contributions in recent payroll records
-
Confirm termination reason is accurately stated
-
Ensure employee details are complete and updated
Within the First Week After Exit
-
Prepare employment confirmation and termination documents
-
Ensure final payroll reflects accurate statutory contributions
-
Address any discrepancies in contribution history promptly
When the Employee Is Ready to Claim
-
Guide the employee to claim via official PERKESO channels (EIS/SIP portal)
-
Assist if contribution records or employment dates need clarification
-
Provide confirmation if requested by PERKESO
A well-prepared HR team reduces stress for employees and avoids post-exit disputes.
Why HR Systems Matter for EIS Compliance
Managing EIS manually increases the risk of:
-
Missed contributions
-
Incorrect payroll deductions
-
Incomplete records during termination
A connected HRMS like Pandahrms helps employers:
-
Automate payroll calculations for EIS, SOCSO, EPF, and EIS
-
Maintain accurate contribution history
-
Generate clean payslips and statutory reports
-
Support HR during exits, audits, and employee claims
By centralising attendance, leave, payroll, and employee profiles, Pandahrms ensures statutory compliance is not dependent on manual tracking or last-minute checks.
Conclusion: EIS Is a Payroll Obligation — and an HR Responsibility
EIS is more than a deduction line on the payslip. It is a statutory safeguard for employees and a compliance responsibility for employers.
When managed correctly:
-
Employees receive timely support after job loss
-
Employers avoid disputes, delays, and penalties
-
HR teams operate with confidence and clarity
With structured payroll processes and a reliable HR system like Pandahrms, managing EIS becomes part of a compliant, professional HR operation — not a year-end headache.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can an employee claim EIS after resigning?
Generally, no. EIS is intended for involuntary job loss, not voluntary resignation or dismissal for serious misconduct.
2. How can employees check if EIS contributions are paid correctly?
Employees should review their monthly payslip for the EIS deduction line. HR can provide contribution confirmation if needed.
3. What happens if an employer pays EIS late?
Late payments may affect claim processing and expose the employer to compliance issues with PERKESO.




